News Releases
Mitsubishi Electric Achieves All Success Criteria for Orbital Demonstration of the Laser Source Module for Space Optical CommunicationUse of off-the-shelf components and nanosatellite help realize lower costs and faster development
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE No. 3725
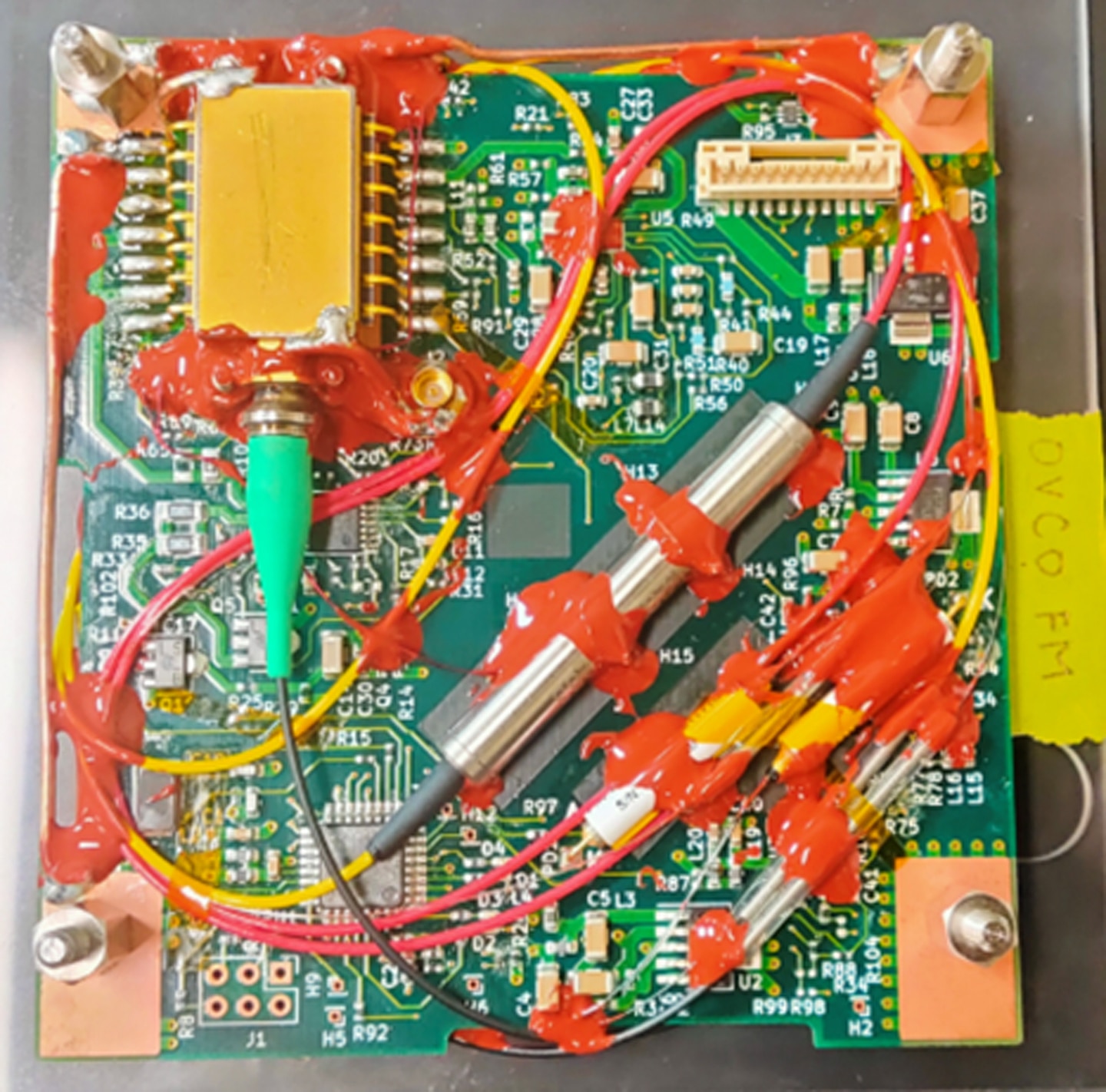
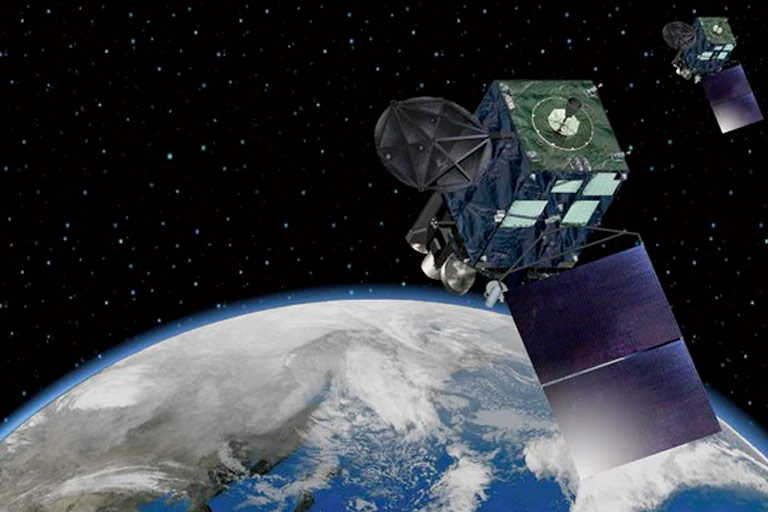
Laser source module implemented on nanosatellite
TOKYO, September 19, 2024 - Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (TOKYO: 6503) announced today that all success criteria,1 including an additional success,2 were achieved without performance degradation during a six-month on-orbit demonstration of its laser source module after extensive evaluation. Mitsubishi Electric conducted the test last year with a module it developed using low-cost commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components. This is the first time in the world3 that the performance degradation of optical components in a space environment has been evaluated.
To improve satellite communication, Mitsubishi Electric has been developing optical devices utilizing versatile, high-performance 1.5μm-wavelength lasers originally produced for land-based fiber-optic communication. After developing an optical receiver in May 2022, the company began developing a laser source module with COTS components for installation in a nanosatellite measuring only 10 x 10 x 34cm (WxDxH). The goals were to develop a laser source module capable of withstanding the extreme conditions of space, particularly radiation and thermal vacuum, and to demonstrate the module's viability in less time and at lower cost than conventional products.4
For the demonstration, the module was installed in the OPTIMAL-15 nanosatellite, which was developed through an industry-academia collaboration. The nanosatellite was launched early last year and an on-orbit demonstration of the module's laser optical frequency control, critical for space communication, was carried out over a six-month period beginning in January 2023. An extensive evaluation of the module's performance has now confirmed that the demonstration not only met all of its success criteria, but also exceeded initial expectations by additionally demonstrating that the module's optical performance was not degraded after six months of operation in space. The company will continue to pursue technological development aimed at the early realization of high-capacity space optical communication.
- 1Specific criteria and targets for evaluating the success of a project, mainly in the field of space science. See "Success criteria for on-orbit demonstration" on page 3/4.
- 2Results that meet or exceed targets for multiple levels of criteria based on degree of difficulty.
- 3According to Mitsubishi Electric's research as of September 19, 2024.
- 4Compared to previous demonstrations conducted in space by Mitsubishi Electric.
- 5Led by ArkEdge Space Inc. and selected for the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry's Subsidy Program for Industrial Technology Practical Application Development (Space Industry Technology Information Infrastructure Development Research and Development Project), the project focused on the theme of "Demonstration of Ultra-Small Satellite Propulsion Systems, Communication Devices, and On-Orbit Advanced Information Processing Technologies using the TRICOM Satellite." The project involved collaboration with Pale Blue Inc., Seiren Co., Ltd., Fukui University, the University of Tokyo Graduate School of Engineering, and Mitsubishi Electric. The nanosatellite was released into space from the International Space Station (ISS) "Kibo" Japanese Experiment Module on January 6, 2023.
Note
Note that the press releases are accurate at the time of publication but may be subject to change without notice.











